2-甲基-4-异噻唑啉-3-酮盐酸盐,2-Methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one hydrochloride [MIT];≥99%
最近浏览商品
-
 O-糖苷酶来源于肺炎链球菌,O-Glycosidase from Streptococcus pneumoniae;recombinant, expressed in E. coli, buffered aqueous solution
O-糖苷酶来源于肺炎链球菌,O-Glycosidase from Streptococcus pneumoniae;recombinant, expressed in E. coli, buffered aqueous solution -
![显示明细 硅油 [二甲基硅油],Silicone oil [Element14® PDMS 1000];viscosity ~1000 cSt 图片 硅油 [二甲基硅油],Silicone oil [Element14® PDMS 1000];viscosity ~1000 cSt](https://www.bszh.cn/images/thumbs/0008464_-silicone-oil-element14-pdms-1000viscosity-1000-cst_32.jpeg) 硅油 [二甲基硅油],Silicone oil [Element14® PDMS 1000];viscosity ~1000 cSt
硅油 [二甲基硅油],Silicone oil [Element14® PDMS 1000];viscosity ~1000 cSt -
 丙二醛四丁基铵盐,Malondialdehyde tetrabutylammonium salt;analytical standard, ≥97.0% (NT)
丙二醛四丁基铵盐,Malondialdehyde tetrabutylammonium salt;analytical standard, ≥97.0% (NT) -
![显示明细 N-(2,6-二氯苯基)-2-吲哚酮 [吲哚酮],N-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-2-indolinone;analytical standard, ≥98.0% (HPLC) 图片 N-(2,6-二氯苯基)-2-吲哚酮 [吲哚酮],N-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-2-indolinone;analytical standard, ≥98.0% (HPLC)](https://www.bszh.cn/images/thumbs/0009033_n-26-2-n-26-dichlorophenyl-2-indolinoneanalytical-standard-980-hplc_32.png) N-(2,6-二氯苯基)-2-吲哚酮 [吲哚酮],N-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-2-indolinone;analytical standard, ≥98.0% (HPLC)
N-(2,6-二氯苯基)-2-吲哚酮 [吲哚酮],N-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-2-indolinone;analytical standard, ≥98.0% (HPLC) -
![显示明细 N-(2,6-二甲基苯基)氯乙酰胺 [利多卡因杂质H],N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)chloroacetamide;99% 图片 N-(2,6-二甲基苯基)氯乙酰胺 [利多卡因杂质H],N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)chloroacetamide;99%](https://www.bszh.cn/images/thumbs/0010550_n-26-hn-26-dimethylphenylchloroacetamide99_32.jpeg) N-(2,6-二甲基苯基)氯乙酰胺 [利多卡因杂质H],N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)chloroacetamide;99%
N-(2,6-二甲基苯基)氯乙酰胺 [利多卡因杂质H],N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)chloroacetamide;99% -
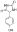 5-(4-羟苯基)乙内酰脲,5-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-2,4-imidazolidinedione;≥98.0%
5-(4-羟苯基)乙内酰脲,5-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-2,4-imidazolidinedione;≥98.0%

